

Classic Bluetooth provides low-latency, cost-effective audio and data transmission, and is compatible across mainstream devices.
Classic Bluetooth protocol is a short-range wireless communication standard used for voice and data transmission between devices. It operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM frequency band, utilizes frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) technology for enhanced anti-interference capability, supports point-to-point, piconet, and scatternet topologies, and offers transmission rates of up to 1-3 Mbps. The protocol provides various standardized profiles for different application scenarios, features cross-platform compatibility, enables fast pairing and stable connections, and enhances user experience.
Application Scenario

Classic Bluetooth is widely used in wireless headphones, speakers, audio systems, and car entertainment systems, providing high-quality audio transmission.

Bluetooth keyboards, mice, and game controllers interact with computers or tablets wirelessly, enhancing convenience of use.
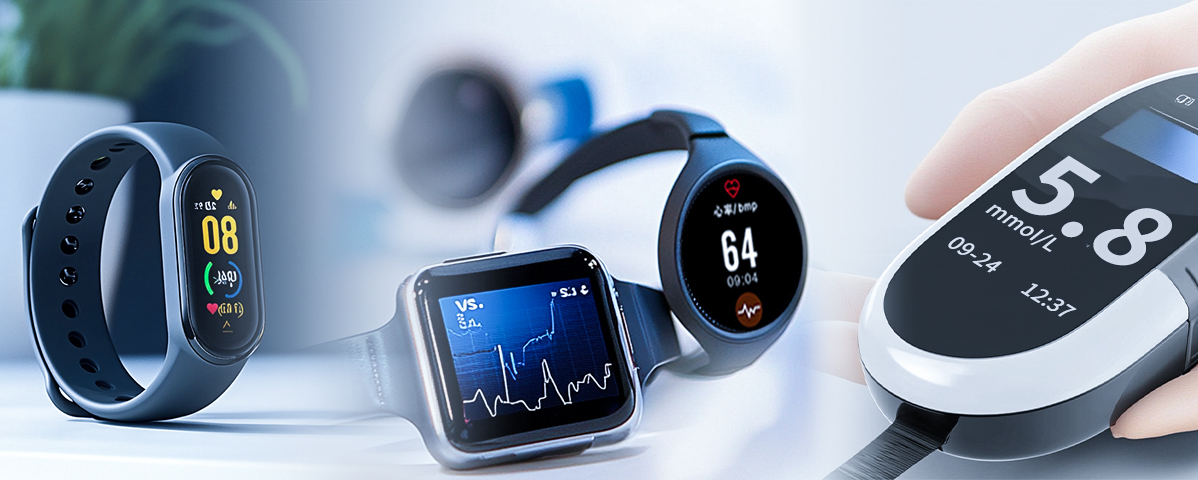
For example, blood glucose monitors, heart rate monitors, and watches can achieve convenient data recording and analysis through wireless connections.

For example, printers and file sharing devices allow users to easily share photos, videos, and documents.

Classic Bluetooth is widely used in wireless headphones, speakers, audio systems, and car entertainment systems, providing high-quality audio transmission.

Bluetooth keyboards, mice, and game controllers interact with computers or tablets wirelessly, enhancing convenience of use.

For example, blood glucose monitors, heart rate monitors, and watches can achieve convenient data recording and analysis through wireless connections.

For example, printers and file sharing devices allow users to easily share photos, videos, and documents.
Basic Working Principle
The topology structure of classic Bluetooth is mainly designed based on the master-slave mode, supporting point-to-point and piconet. Point-to-point refers to a scenario where one master device connects to one slave device. A piconet consists of one master device and multiple slave devices. A Scatternet is a composite network consisting of multiple piconets, where devices can play different roles in different piconets. The master device manages clock synchronization and hopping sequences, coordinating communication timing through a polling mechanism. The system utilizes time-division multiplexing technology to achieve alternating data transmission between master and slave devices.


The classic Bluetooth protocol is divided into three main parts: the Application Layer, the Host Layer, and the Controller Layer. The Application Layer is directly user-facing and implements specific functions, including the logic to achieve these functions and standardized profiles for interaction between devices. The Host Layer includes components such as GAP, SM, SDP, L2CAP, and HCI, offering a comprehensive set of functions for standardized device management, service discovery, security management, data segmentation, and reassembly. The Controller Layer's main functions include RF frequency selection, transmission power control, link management, frequency hopping sequence management, and clock synchronization.
Specification Parameters

- Enhanced Data Rate
- Secure Simple Pairing
- Security Mode 4
- Extended Inquiry Response
- Flushable Packet

- A2DP
- AVRCP
- HFP
- PBAP
- SPP
- iAP
- HID
- MAP
- OPP
- PAN
Advantages

Comprehensive profile system, rich audio encoding, suitable for different application scenarios.

Profiles can be configured according to application scenarios, with high flexibility and low code resource consumption.

After years of product iteration and optimization, the performance is stable and reliable, with good compatibility.

Bidirectional data transmission rate: sending and receiving speeds both can reach up to 120KB/s; Unidirectional data transmission rate: can reach up to 200KB/s.
Product Applications













 苏公网安备32059002006558号
苏公网安备32059002006558号