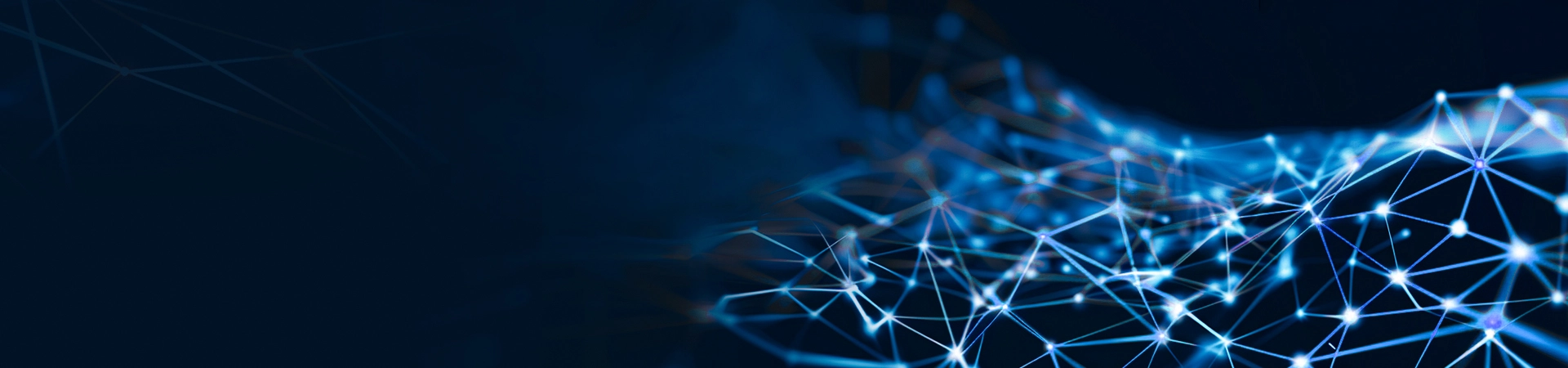


Based on the Thread protocol, the smart home mesh network supports multiple application layer protocol those are based on IP protocols, ensuring high scalability and security to guarantee stable and reliable whole-home connectivity.
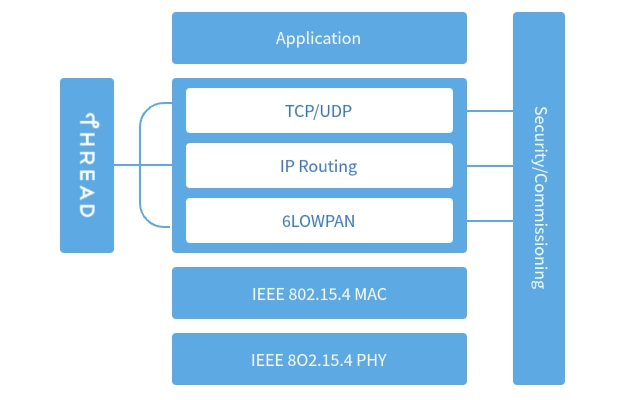
Thread is a low-power wireless mesh networking technology built on open standard IP protocols, designed specifically for smart homes and the Internet of Things (IoT). It supports reliable, cost-effective, and low-energy communication between devices. Thread utilizes the IEEE 802.15.4 standard for its PHY and MAC layers, combined with 6LoWPAN technology (IPv6 over Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Networks), to ensure excellent compatibility with IPv6 devices such as smartphones, computers, and internet infrastructure.
Application Scenario
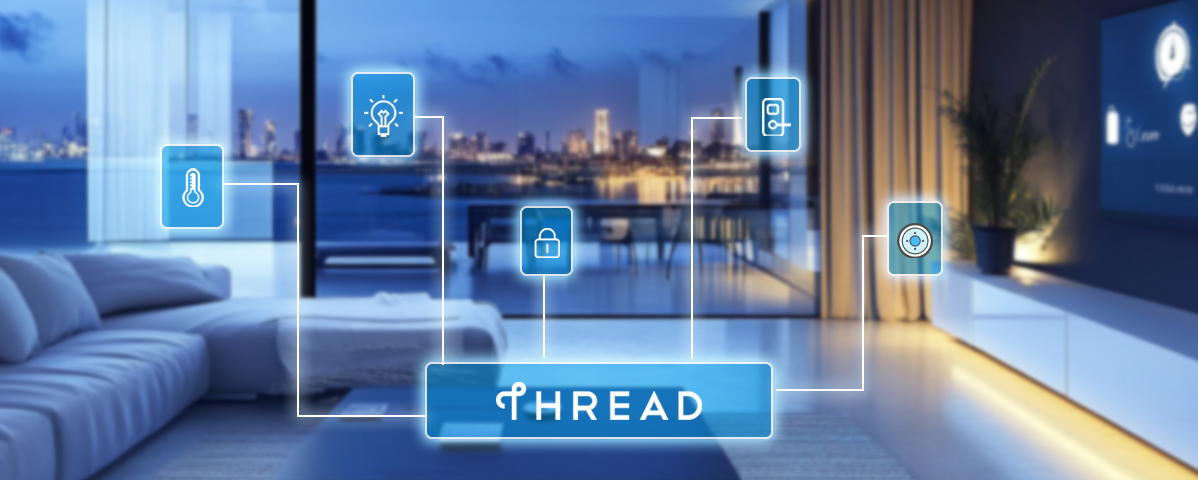

Thread is specifically designed for low-power smart home devices such as lighting, thermostats, and door locks. Its mesh network supports self-healing of faulty nodes, ensuring reliable connectivity.
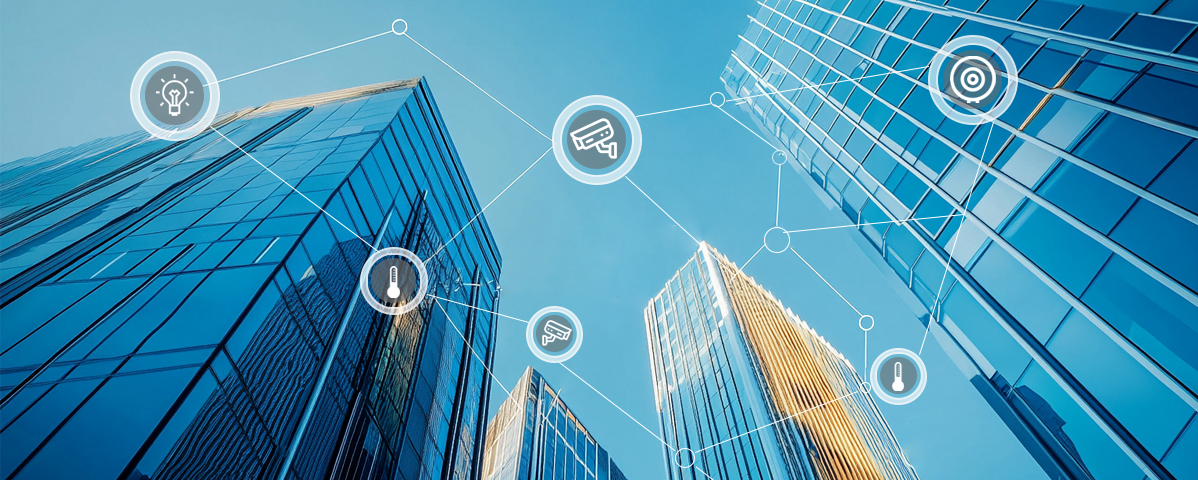

Thread is suitable for large commercial building automation scenarios, such as lighting, HVAC, security, and asset tracking. Its high scalability and reliability enable stable communication among a large number of devices.

Thread enables secure connection of devices to the internet and cloud through a Border Router, supporting functions like remote monitoring and firmware updates. Its 1.3.0 and 1.4 versions standardize Border Router design, further simplifying the integration process with IP infrastructure.
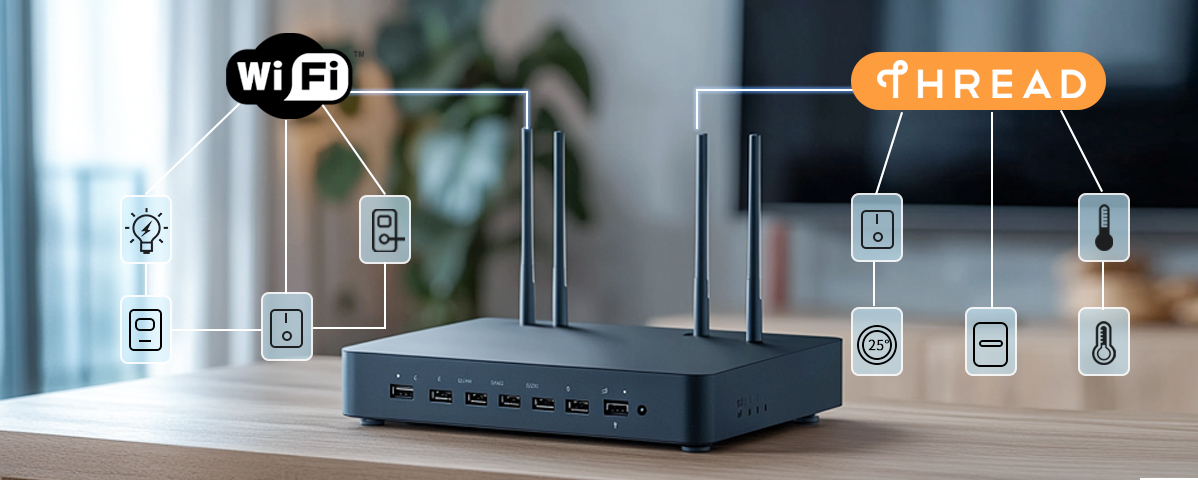

Thread is based on the IPv6 protocol and seamlessly integrates with existing IP networks such as Wi-Fi and Ethernet. The Border Router provides bidirectional IPv6 connectivity, supporting device interoperability across networks, such as connecting Wi-Fi Matter devices with Thread Matter devices in a home environment.

As a network layer protocol, Thread supports multiple application layer protocols (such as Matter, KNX IoT, DALI+) to run concurrently on a single network, enhancing the interoperability of devices from different vendors.

Thread is specifically designed for low-power smart home devices such as lighting, thermostats, and door locks. Its mesh network supports self-healing of faulty nodes, ensuring reliable connectivity.

Thread is suitable for large commercial building automation scenarios, such as lighting, HVAC, security, and asset tracking. Its high scalability and reliability enable stable communication among a large number of devices.

Thread enables secure connection of devices to the internet and cloud through a Border Router, supporting functions like remote monitoring and firmware updates. Its 1.3.0 and 1.4 versions standardize Border Router design, further simplifying the integration process with IP infrastructure.

Thread is based on the IPv6 protocol and seamlessly integrates with existing IP networks such as Wi-Fi and Ethernet. The Border Router provides bidirectional IPv6 connectivity, supporting device interoperability across networks, such as connecting Wi-Fi Matter devices with Thread Matter devices in a home environment.

As a network layer protocol, Thread supports multiple application layer protocols (such as Matter, KNX IoT, DALI+) to run concurrently on a single network, enhancing the interoperability of devices from different vendors.
Basic Working Principle
The Thread protocol builds a low-power IPv6 network based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. It uses a 6LoWPAN adaptation layer to compress IPv6 headers, thereby reducing transmission overhead, and performs fragmentation and reassembly when data packets exceed the maximum transmission unit (MTU) of the MAC layer. Additionally, the protocol utilizes a Mesh Header at the link layer for multi-hop data forwarding, which reduces the load on the network layer, while the combination of IP routing and 6LoWPAN link-layer forwarding enhances transmission efficiency. Network devices support automatic IPv6 address configuration and transmit data through routing protocols. Security mechanisms protect data frames at the MAC layer using a network-wide key, while the DTLS protocol ensures the security of the commissioning process. New devices require authorized configuration and are uniformly managed by a Commissioner for network entry and parameter transmission.
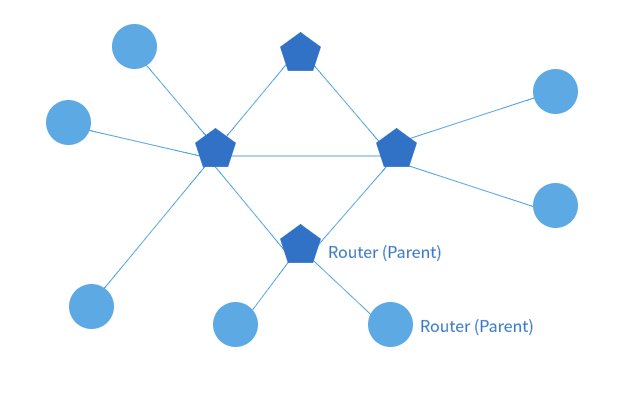
The Thread network comprises two roles: Routers and End Devices. Routers act as the backbone of the network and remain always on, responsible for routing data packets. The Thread network can support up to 32 active routers to form a mesh topology, providing redundancy and self-healing capabilities. Routers optimize message forwarding by maintaining a routing table.
End Devices rely on a parent router for communication and can be classified into Router-Eligible End Devices (REEDs) and Sleepy End Devices (SEDs). REEDs have the capability to upgrade to a router, while SEDs are low-power devices that remain active only when necessary and do not participate in routing.
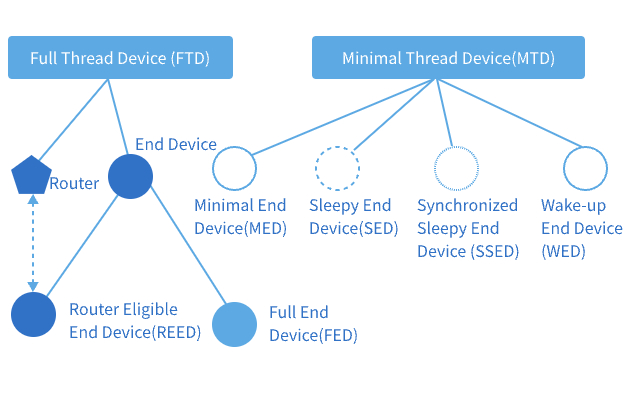
Thread network devices are classified into Full Thread Device (FTD) and Minimal Thread Device (MTD). An FTD can function as a Router, a Router-Eligible End Device (REED), or a Full End Device (FED), and is responsible for maintaining links to neighboring routers. In contrast, an MTD has lower hardware requirements and power consumption, operating as an End Device (ED) that communicates through a parent router and wakes periodically to synchronize. End devices are classified into three types: Sleepy End Devices (SED), Synchronized Sleepy End Devices (SSED), and Wake-up End Devices (WED). The SSED utilizes the Coordinated Sampled Listening (CSL) mode for data reception, allowing it to precisely manage its sleep-wake cycles for higher power efficiency. WED (Wake-up End Device) is a type of device that offers a time-slotted synchronous transmission mode. Its core characteristic is the ability to be directly awakened for a connection by a Wake-up Coordinator (WC), such as a smartphone, even in the absence of an existing Thread network. After the control operation is complete, the WED can quickly return to a lower-power, wake-up listening state. This mechanism not only provides WED with advantages like low power consumption, high flexibility, and strong adaptability, but also enables better support for multi-protocol coexistence.
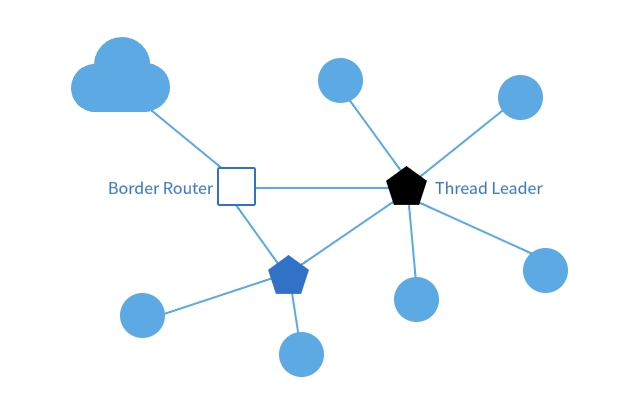
A Border Router is responsible for interconnecting Thread network nodes with external IP networks (Internet/LAN/VPN) and forwarding data. Leveraging the same IPv6 protocol eliminates the need for protocol translation, simplifying communication processes.
A Thread network can also support multiple active Border Routers to provide redundancy and resilience, avoiding single points of failure. Border Routers may additionally offer application-layer services (e.g., Thread device discovery proxies). During commissioning, when the Commissioner resides on an external network, the Border Router acts as a secure intermediary to assist device onboarding. Simultaneously, Border Routers can participate in external routing protocols, announcing global IPv6 prefixes and assigning addresses to network nodes.
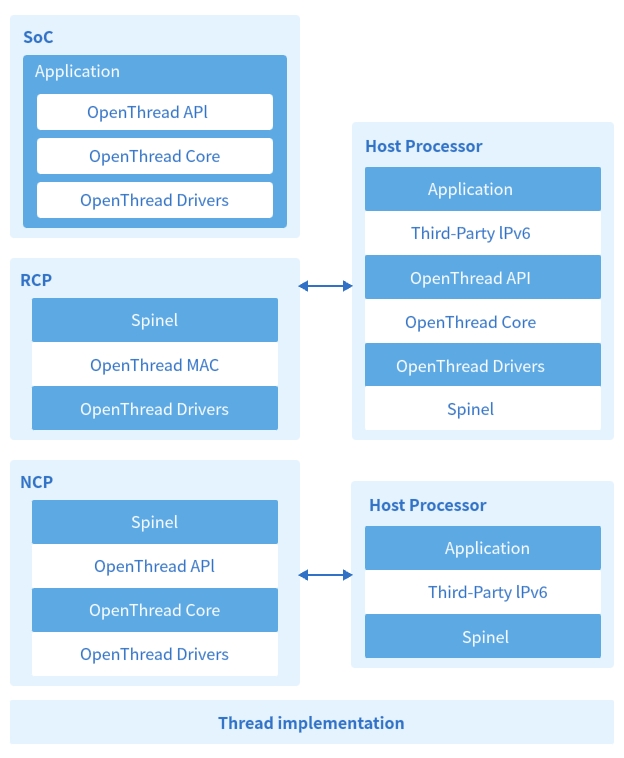
Thread network implementations are categorized into three hardware architectures:
System-on-Chip (SoC): Integrates radio frequency (RF), processor, and protocol stack into a single chip. Operated directly via Thread APIs, it offers low power consumption, cost-effectiveness, and multi-protocol coexistence (e.g., Wi-Fi/Bluetooth). Ideal for end devices like sensors.
Radio Co-Processor (RCP): Deploys the protocol stack on the host processor while retaining MAC layer control on the RF module. Communication occurs via SPI/UART interfaces using the Spinel protocol. The host processor remains active to ensure reliability, making it suitable for compute-capable devices like video hubs.
Network Co-Processor (NCP): Runs the full OpenThread protocol stack on a co-processor. The host processor sends commands via UART/SPI and can enter sleep mode, while the co-processor maintains network connectivity. Designed for multi-task devices such as gateways or IP cameras.
Specification Parameters

- Compliance with the IEEE 802.15.4-2015 specification
- Hardware CSMA-CA mechanism, automatic ACK response, and FCS check
- Support for all CCA modes (ED/CS/Combined Mode) and per packet RSSI/LQI report
- Hardware AES-CCM security engine
- Coexistence mechanism for multi-protocol PHY layers

- Fully support Zigbee Pro and Zigbee 3.0 protocols
- Fully support for the latest Thread protocol (Thread 1.4)
- Other protocols based on IEEE 802.15.4, e.g., RF4CE
Advantages

Support to run Thread (or Zigebee) and BLE Protocol concurrently.

Providing a complete solution for smart home IoT with low power consumption and high performance.

Offers a variety of peripherals and provides comprehensive application examples to accelerate IoT product development.
Product Applications





Implementation Guide
To implement a basic Thread network, please refer to the sample projects section in the Thread protocol documentation.
To connect the Thread network to the external internet via a Border Router, refer to the OpenThread Border Router's sample project section in the documentation.
Recommended Hardware
Part Number | RTL8771HTV | RTL8771GTV | RTL8771GUV | RTL8777GKF | RTL8772GWP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Thread Implementation Architecture | RCP | RCP | RCP | SoC | SoC |
Application | (Co-work with Host) Thread Border Router Thread Router Thread End Devices | (Co-work with Host) Thread Border Router Thread Router Thread End Devices | (Co-work with Host) Thread Border Router Thread Router Thread End Devices | Matter devices Thread Router Thread End Devices | Matter devices Thread Border Router Thread Router Thread End Devices |
Host Interface | UART | UART | USB | - | - |
Multi-Protocol | - | - | - | BLE+Thread | BLE+Thread |
TX Power (Max) | 8dBm | 14dBm | 14dBm | 14dBm | 14dBm |
Display Interface | - | - | - | - | I8080 MIPI SDI |


 苏公网安备32059002006558号
苏公网安备32059002006558号