

1 Background
Bluetooth audio technology has made remarkable progress over the past few decades and has been widely applied in various consumer electronic devices. Codec offloading, an important technology in modern Bluetooth audio devices, is becoming increasingly popular. It enhances the performance and efficiency of devices by transferring the computational tasks of audio encoding and decoding from the main processor to dedicated hardware components or coprocessors.
2 Introduction
The RTL8761C is a highly integrated single-chip Bluetooth 5.4 controller that connects to the host via UART/USB and PCM/I2S interfaces for transmitting Bluetooth HCI packets and audio data. It also integrates multiple audio codecs to meet the needs of different scenarios.
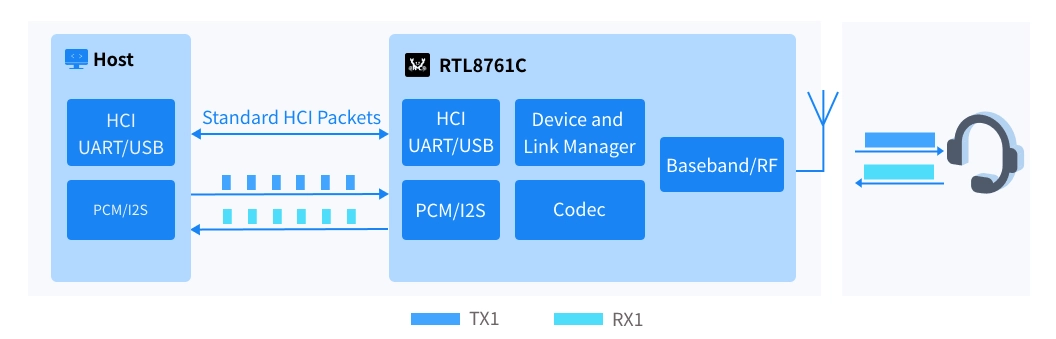
The Host interacts with the RTL8761C through HCI for control signaling to establish an eSCO or ISO connection. After the connection is established, the Host exchanges audio data with the RTL8761C through the PCM/I2S interface. The RTL8761C encodes the audio data received from the Host and transmits it via a wireless link. Meanwhile, the audio received over the air is decoded and then returned to the Host via PCM/I2S.
In addition, the RTL8761C supports time-division multiplexing, allowing two eSCO connections to share the same set of PCM/I2S interfaces. This method effectively improves the utilization rate of the existing PCM channel and reduces the demand for additional hardware resources. To further optimize performance and energy consumption, the RTL8761C is equipped with an LC3 codec for LE Audio and also supports time-division multiplexing, enabling two ISO connections to share the same PCM/I2S interface, thereby achieving efficient audio transmission.
3 Application Scenarios
The RTL8761C, through the combination of codec offloading and PCM/I2S time-division multiplexing, can stably support dual eSCO/ISO connections on resource-constrained platforms, especially suitable for complex real-time audio scenarios such as dual voice calls, while taking into account power consumption, latency and stability.
1. Two mobile phones can be engaged in calls simultaneously.
While driving, the driver can simultaneously connect to two phone lines and quickly switch between them without having to disconnect and reconnect each time. This can enhance the flexibility of call handling, reduce distractions to the driver, and improve driving safety.
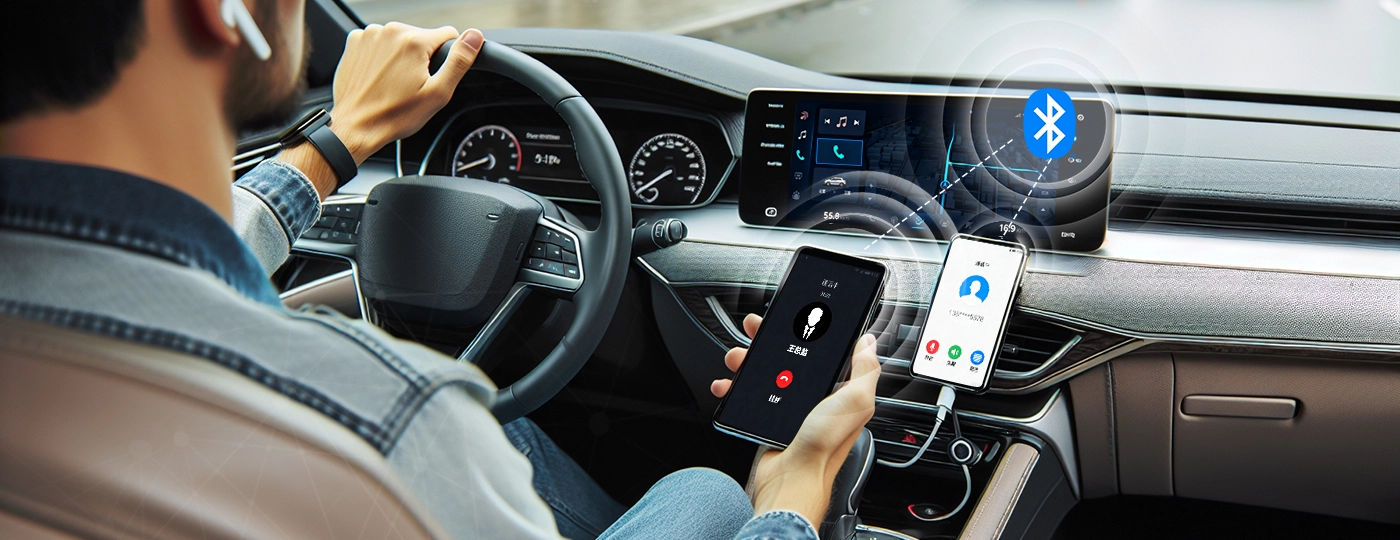

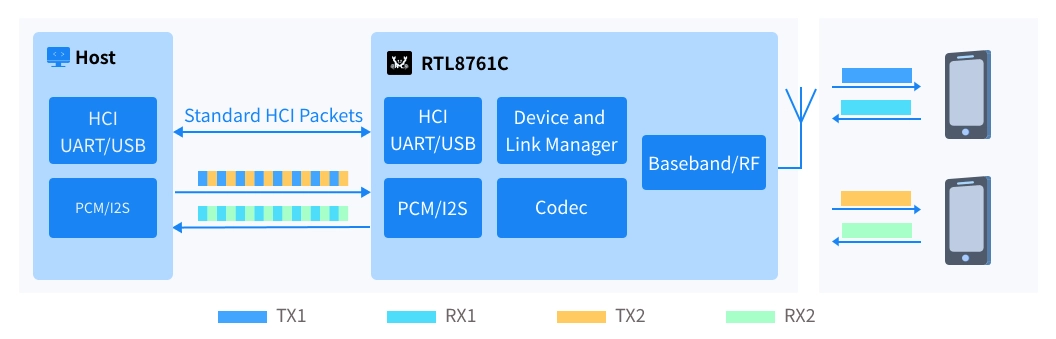
The simple process is as follows:
1) Pairing and connection stage
Mobile phone 1 ←→ Car Bluetooth Device ←→ Mobile phone 2
2) Call process of mobile phone 1
Mobile phone 1 → RTL8761C decoding → Host → Speaker playback
Microphone collection → Host → RTL8761C encoding → Mobile phone 1
3) Parallel call process of mobile phone 2
Mobile phone 2 → RTL8761C decoding → Host → Speaker playback
Microphone collection → Host → RTL8761C encoding → Mobile phone 2
4) User operation
Suspend one of the calls through the device menu, or keep two calls simultaneously
2. Helmet intercom
During a motorcycle ride, the rider and rear passenger can communicate through the helmet connected to the onboard Bluetooth device. This can avoid the interference from external noise, allowing the rider and passengers to communicate easily while on the move. Meanwhile, it can also reduce the impact on the driver's operation and enhance riding safety.
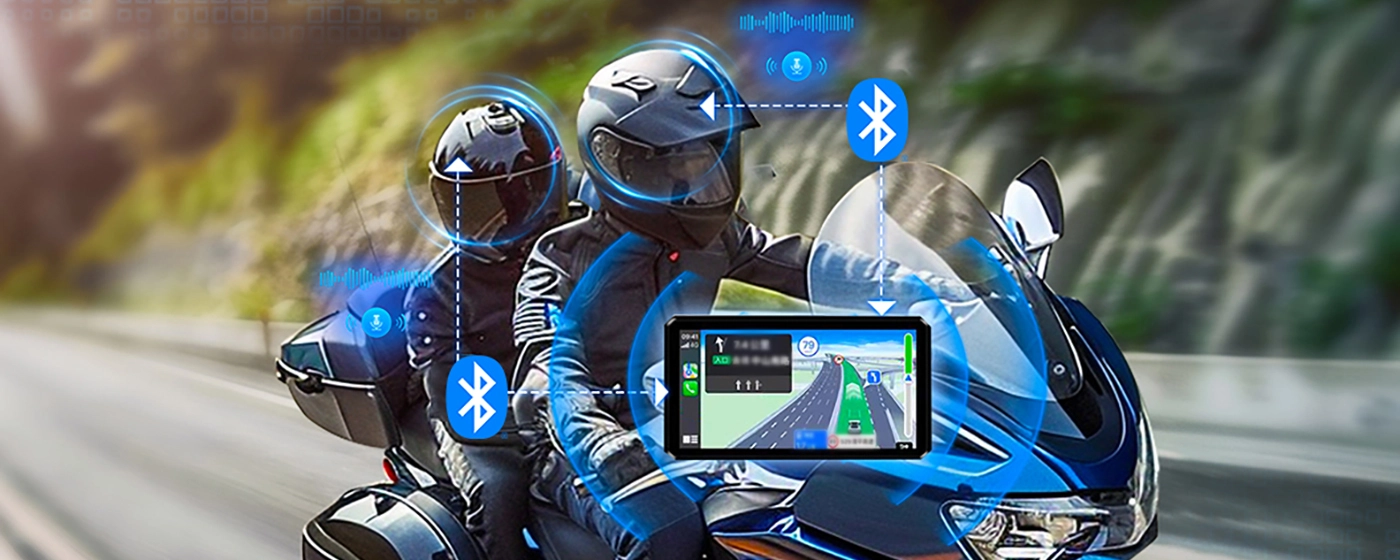

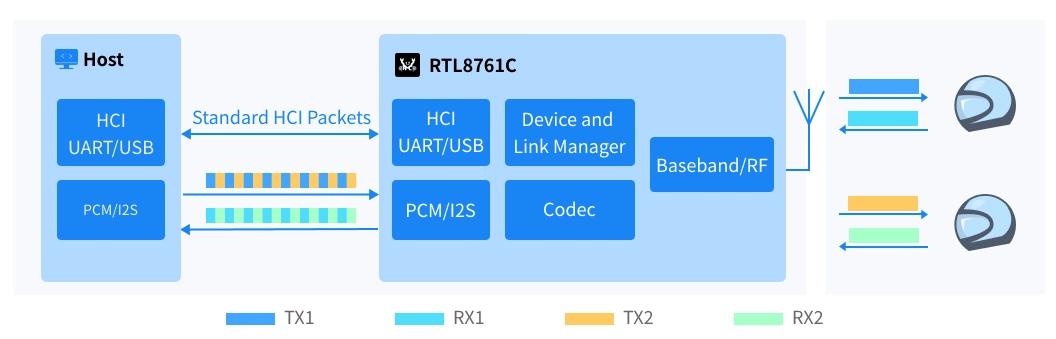
The simple process is as follows:
1) Pairing and connection stage
Helmet 1 ←→ Car Bluetooth device ←→ Helmet 2
2) Intercom process
Helmet 1 → RTL8761C decoding → Host Channel switching → RTL8761C encoding → Helmet 2
Helmet 2 → RTL8761C decoding → Host Channel Switching → RTL8761C encoding → Helmet 1
3) User operation
Select to turn the intercom on or off through the device menu
4 Advantages
The RTL8761C supports codec offloading technology, enhancing the smoothness and speed of audio processing, ensuring the stability of transmission, and reducing latency. It has significant advantages for applications that require real-time response and high-definition audio streams:
1. Reduce the load on the main processor: By offloading encoding/decoding to the Bluetooth controller, the host CPU can enter a sleep mode, thereby reducing the standby power consumption of the entire machine.
2. Power-saving for long-term playback: In scenarios such as continuous music playback and voice calls, hardware encoding and decoding have high efficiency, and the power consumption per unit is lower than that of software encoding.
3. Enhance battery life of the equipment: The receiving end directly decodes and outputs on the controller without going through the main memory and bus, thereby reducing the overall energy consumption.
5 Outlook
In increasingly complex audio scenarios requiring extremely high real-time performance, if the host system is only solely responsible for high-level resource orchestration, routing strategies, and scenario determination, while key real-time audio processing tasks, such as encoding and decoding, are delegated to the Bluetooth controller to execute, this approach can not only significantly reduce the wake-up frequency and data transfer of the host CPU, but also reduce power consumption and heat generation. It can also maintain a more stable low-latency performance, ensuring smooth synchronization and switching between multiple streams.
As LE Audio enters multi-device sharing scenarios, codec offloading will be elevated from a performance optimization option to a standard capability of the Bluetooth audio architecture, becoming the core competitive advantage of future solutions.
6 Terminology Definitions
1. Host
The upper-level logic and protocol stack in a Bluetooth system are usually located in the application processor or within the operating system environment.
2. HCI (Host Controller Interface)
The standardized interface and protocol layer that connects the Host and the Controller.
3. eSCO (Extended Synchronous Connection-Oriented)
An extended version of the Synchronous Connection-Oriented link for Bluetooth BR/EDR, used for real-time transmission of voice and other time-sensitive applications that require fixed time slots and low latency.
4. ISO (LE Isochronous Channel/Data)
The isochronous transmission mechanism introduced by LE Audio ensures that data arrives at a fixed rhythm, meeting the requirements of low latency and time alignment.
5. PCM/I2S (Digital Audio Interface)
PCM (Pulse Code Modulation): A synchronous serial voice interface on the baseband side, used for interacting with external voice codecs/basebands.
I2S (Inter-IC Sound): A digital audio standard interface, including LRCLK, BCLK, and DATA lines, for transmitting stereo PCM data.


 苏公网安备32059002006558号
苏公网安备32059002006558号